使う度に調べるので、メモしておきます。
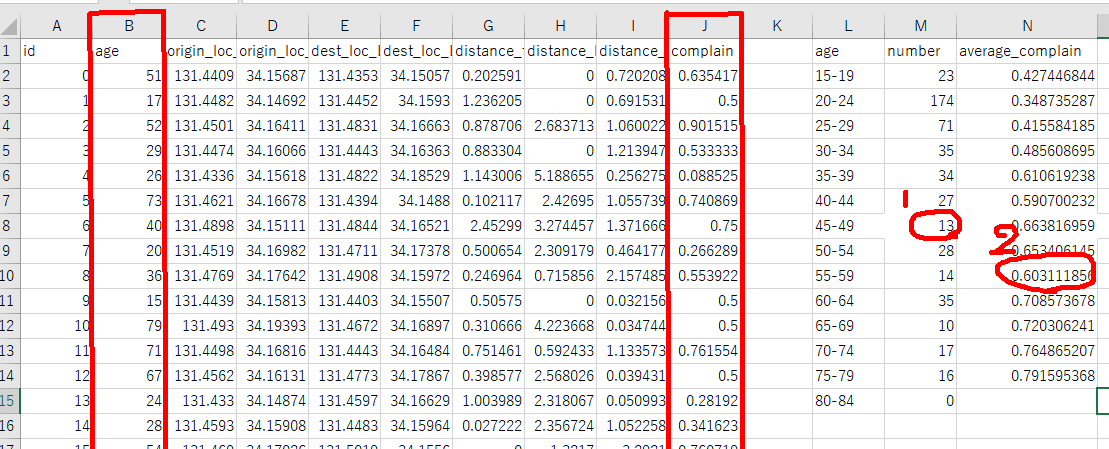
1. 40歳から44歳の人の人数を数えろ
=COUNTIFS($B$1:$B$498, ">=45",$B$1:$B$498, "<50" )
2.55歳から59歳の人の不満値の平均値を求めよ
=AVERAGEIFS($J$1:$J$498, $B$1:$B$498, ">=55",$B$1:$B$498, "<60" )
Keywords: COUNTIF, COUNTIFS, AVERAGEIFS
江端智一のホームページ
使う度に調べるので、メモしておきます。

1. 40歳から44歳の人の人数を数えろ
=COUNTIFS($B$1:$B$498, ">=45",$B$1:$B$498, "<50" )
2.55歳から59歳の人の不満値の平均値を求めよ
=AVERAGEIFS($J$1:$J$498, $B$1:$B$498, ">=55",$B$1:$B$498, "<60" )
Keywords: COUNTIF, COUNTIFS, AVERAGEIFS
This program is based on the following page
https://qiita.com/ufoo68/items/9e4ca04578ba0f5fa5ff
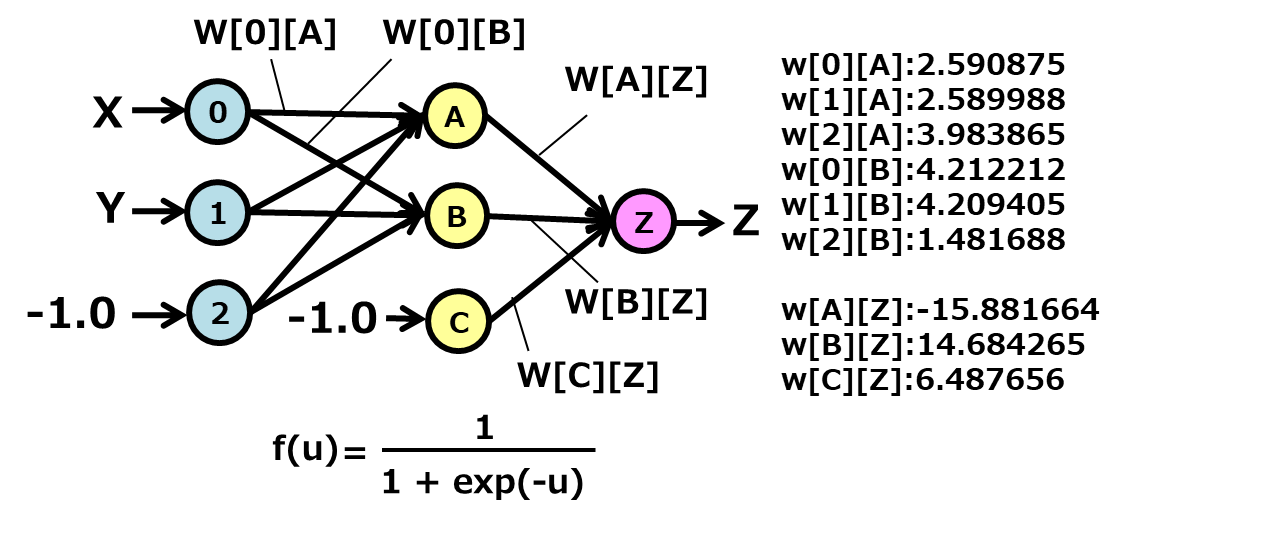
This program solves the XOR problem using MLP with one hidden layer.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//num of units
#define NUM_INPUT 2
//#define NUM_HIDDEN 20
#define NUM_HIDDEN 2
double sigmoid(double x) {
return 1/(1+exp(-x));
}
//derivative of sigmoid function
double d_sigmoid(double x) {
double a = 0.1;
return a*x*(1-x);
}
int main(void) {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
//train data
double train_x[4][NUM_INPUT+1] = {{0, 0, -1},{0, 1, -1},{1, 0, -1},{1, 1, -1}};
double d[4] = {0, 1, 1, 0};
//net
double w[NUM_HIDDEN+1][NUM_INPUT+1];
double v[NUM_HIDDEN+1];
double y[4][NUM_HIDDEN+1];
double z[4];
double eta = 0.1;
int epoch = 1000000;
//other
int i, j, k, l;
double tmp = 0;
//update weights using rand()
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN+1; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
w[l][i] = ((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1));
}
}
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
v[i] = ((double)rand() / ((double)RAND_MAX + 1));
}
//tain
for(k=0; k<epoch; k++) {
//feedforward
for(j=0; j<4; j++) {
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
tmp += train_x[j][i] * w[l][i];
}
y[j][l] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
y[j][NUM_HIDDEN] = -1;
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
tmp += y[j][i] * v[i];
}
z[j] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
//backward
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
v[i] = v[i] - eta * y[j][i] * d_sigmoid(z[j]) * (z[j] - d[j]);
}
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_INPUT+1; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
w[i][l] = w[i][l] - eta * train_x[j][l] * d_sigmoid(y[j][i]) * d_sigmoid(z[j]) * (z[j] - d[j]) * v[i];
}
}
}
/*
//print detail
printf("z=");
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
printf("%f ", z[i]);
}
printf("epoch:%d\n",k);
*/
}
//predict
for(j=0; j<4; j++) {
//hidden
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN; l++) {
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
tmp += train_x[j][i] * w[l][i];
}
y[j][l] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
y[j][NUM_HIDDEN] = -1;
//output
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
tmp += y[j][i] * v[i];
}
z[j] = sigmoid(tmp);
tmp = 0;
}
//print result
printf("z=");
for(i=0; i<4; i++) {
printf("%f ", z[i]);
}
printf("epoch:%d\n",k);
for(i=0; i<NUM_INPUT+1; i++) {
for(l=0; l<NUM_HIDDEN+1; l++) {
printf("w[%d][%d]:%f\n", i, l, w[i][l]);
}
}
for(i=0; i<NUM_HIDDEN+1; i++) {
printf("v[%d]:%f\n",i, v[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Save this program as a name "mlp.c", compile ">gcc mlp.c" and execute ">./a.exe"
Golang 文字列を数値に変換する方法で、文字列→実数なら、これが一番てっとり早そう
dest_lat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(row[2], 64)
strconv.ParseIntとstrconv.ParseUnitは、文字列を解析して整数型を返す関数
それぞれ符号付き整数型と符号なし整数型に対応している。
I hope you could understand the min-max method of Fuzzy reasoning, using the following Go programming list.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func max_2(a, b float64) float64 {
if a > b {
return a
} else {
return b
}
}
func min_2(a, b float64) float64 {
if a > b {
return b
} else {
return a
}
}
type condition_MF3 struct { // Base class for condition_MF3
center float64
width float64
express string
}
func new_condition_MF3(_center, _width float64, _express string) *condition_MF3 {
c3 := new(condition_MF3)
c3.center = _center
c3.width = _width
c3.express = _express
return c3
}
// Class for the membership function (3 mountains) of the former case
func (c3 *condition_MF3) func_X(_x float64) float64 {
// x,y denote coordinates on the membership function
x := _x
y := 0.0 // The value of y is always greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1
if c3.express == "LESS" {
if x <= c3.center-c3.width {
y = 1.0
} else if x <= c3.center {
y = -1.0 / c3.width * (x - c3.center)
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c3.express == "COMMON" {
if x <= c3.center-c3.width {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c3.center {
y = 1.0/c3.width*(x-c3.center) + 1.0
} else if x <= c3.center+c3.width {
y = -1.0/c3.width*(x-c3.center) + 1.0
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c3.express == "MORE" {
if x <= c3.center {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c3.center+c3.width {
y = 1.0 / c3.width * (x - c3.center)
} else {
y = 1.0
}
} else {
fmt.Println("MF3: wrong expression")
os.Exit(1)
}
return y
}
type condition_MF5 struct { // Base class for condition_MF5
center float64
width float64
express string
}
func new_condition_MF5(_center, _width float64, _express string) *condition_MF5 {
c5 := new(condition_MF5)
c5.center = _center
c5.width = _width
c5.express = _express
return c5
}
func (c5 *condition_MF5) func_X(_x float64) float64 {
// Class for the former membership function (5 mountains)
// x,y are the coordinates on the membership function
x := _x
y := 0.0 // The value of y is always greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1
if c5.express == "LESSLESS" {
if x <= c5.center-2.0*c5.width {
y = 1.0
} else if x <= c5.center-c5.width {
y = -1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center-2.0*c5.width)) + 1.0
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c5.express == "LESS" {
if x <= c5.center-2.0*c5.width {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c5.center-c5.width {
y = 1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center-c5.width)) + 1.0
} else if x <= c5.center {
y = -1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center-c5.width)) + 1.0
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c5.express == "COMMON" {
if x <= c5.center-c5.width {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c5.center {
y = 1.0/c5.width*(x-c5.center) + 1.0
} else if x <= c5.center+c5.width {
y = -1.0/c5.width*(x-c5.center) + 1.0
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c5.express == "MORE" {
if x <= c5.center {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c5.center+c5.width {
y = 1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center+c5.width)) + 1.0
} else if x <= c5.center+2.0*c5.width {
y = -1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center+c5.width)) + 1.0
} else {
y = 0.0
}
} else if c5.express == "MOREMORE" {
if x <= c5.center+c5.width {
y = 0.0
} else if x <= c5.center+2.0*c5.width {
y = 1.0/c5.width*(x-(c5.center+2.0*c5.width)) + 1.0
} else {
y = 1.0
}
} else {
fmt.Println("MF5 func_X(): wrong expression")
os.Exit(1)
}
return y
}
/////////////////////////////
type action_MF5 struct { // Base class for action_MF5
center float64
width float64
express string
x float64
y float64
}
type action_MF3 struct { // Base class for action_MF3
center float64
width float64
express string
x float64
y float64
}
func new_action_MF5(_center, _width float64, _express string) *action_MF5 {
a5 := new(action_MF5)
a5.center = _center
a5.width = _width
a5.express = _express
if a5.express == "LESSLESS" {
a5.x = a5.center - 2.0*a5.width
} else if a5.express == "LESS" {
a5.x = a5.center - a5.width
} else if a5.express == "COMMON" {
a5.x = a5.center
} else if a5.express == "MORE" {
a5.x = a5.center + a5.width
} else if a5.express == "MOREMORE" {
a5.x = a5.center + 2.0*a5.width
} else {
fmt.Println("new_action_MF5: wrong scale expression")
os.Exit(-1)
}
a5.y = 0.0
return a5
}
func new_action_MF3(_center, _width float64, _express string) *action_MF3 {
a3 := new(action_MF3)
a3.center = _center
a3.width = _width
a3.express = _express
if a3.express == "LESS" {
a3.x = a3.center - a3.width
} else if a3.express == "COMMON" {
a3.x = a3.center
} else if a3.express == "MORE" {
a3.x = a3.center + a3.width
} else {
fmt.Println("new_action_MF3: wrong scale expression")
os.Exit(-1)
}
a3.y = 0.0
return a3
}
// The latter membership function (5 mountains) class
func (a5 *action_MF5) func_Y() float64 {
return a5.y
}
// The latter membership function (3 mountains) class
func (a3 *action_MF3) func_Y() float64 {
return a3.y
}
func (a5 *action_MF5) func_Max(b float64) {
a5.y = max_2(b, a5.y)
}
func (a3 *action_MF3) func_Max(b float64) {
a3.y = max_2(b, a3.y)
}
func (a5 *action_MF5) func_X() float64 {
return a5.x
}
func (a3 *action_MF3) func_X() float64 {
return a3.x
}
func fuzzy_reasoning(temp, humi float64) float64 {
// Temperature(former)
Temp_Less := new_condition_MF3(20, 10, "LESS")
Temp_Common := new_condition_MF3(20, 10, "COMMON")
Temp_More := new_condition_MF3(20, 10, "MORE")
// Humidity(former)
Humi_Less := new_condition_MF3(50, 20, "LESS")
Humi_Common := new_condition_MF3(50, 20, "COMMON")
Humi_More := new_condition_MF3(50, 20, "MORE")
// Switch(前件部)
Switch_Less := new_action_MF3(0,1,"LESS")
Switch_Common := new_action_MF3(0,1,"COMMON")
Switch_More := new_action_MF3(0,1,"MORE")
// [Rule 01]
Rule01 := min_2(Temp_More.func_X(temp), Humi_More.func_X(humi))
Switch_Less.func_Max(Rule01) // the latters values are overwritten if the value is large enough.
fmt.Println("Rule01", Rule01)
// [Rule 02]
Rule02 := min_2(Temp_Common.func_X(temp), Humi_More.func_X(humi))
Switch_Common.func_Max(Rule02) // the latters values are overwritten if the value is large enough.
fmt.Println("Rule02", Rule02)
// [Rule 03]
Rule03 := min_2(Temp_More.func_X(temp), Humi_Common.func_X(humi))
Switch_Less.func_Max(Rule03) // the latters values are overwritten if the value is large enough.
fmt.Println("Rule03", Rule03)
// [Rule 04]
Rule04 := min_2(Temp_Less.func_X(temp), Humi_Less.func_X(humi))
Switch_More.func_Max(Rule04) // the latters values are overwritten if the value is large enough.
fmt.Println("Rule04", Rule04)
// Reasoning calculations
numerator :=
Switch_Less.func_X()*Switch_Less.func_Y() +
Switch_Common.func_X()*Switch_Common.func_Y() +
Switch_More.func_X()*Switch_More.func_Y()
denominator :=
Switch_Less.func_Y() +
Switch_Common.func_Y() +
Switch_More.func_Y()
reasoning := numerator / denominator
return reasoning
}
func main(){
fmt.Println(fuzzy_reasoning(27.0, 67.0))
}
A社 CSVファイルパース用テストコード (用事が終わったら消すこと)
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"regexp"
"strings"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("tracking_data.csv")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer file.Close()
r := csv.NewReader(file)
rows, err := r.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
lat := [10000]string{}
lng := [10000]string{}
speed := [10000]string{}
// [][]stringなのでループする
for j, v := range rows {
if j == 0 {
continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
}
//fmt.Println(v[3])
// v[3]をバラバラに分解する
// v3 := regexp.MustCompile("[() ,]").Split(v[3], -1)
v3 := regexp.MustCompile("}, {").Split(v[3], -1)
for i, s := range v3 { // i: 数
//fmt.Printf("%s\n", s)
v31 := strings.Replace(s, "\"lat\": ", "", -1)
v32 := strings.Replace(v31, "\"lng\": ", "", -1)
v33 := strings.Replace(v32, "[{", "", -1)
v34 := strings.Replace(v33, "}]", "", -1)
v35 := regexp.MustCompile(",").Split(v34, -1)
for k, s5 := range v35 {
//f64, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(s5, 64)
//fmt.Println("string", i, s5)
if k == 0 {
lat[i] = s5
} else {
lng[i] = s5
}
}
}
//fmt.Println(lat[0], lng[0], lat[19], lng[19])
//fmt.Println()
// v[4]をバラバラに分解する
v41 := strings.Replace(v[4], "[", "", -1)
v42 := strings.Replace(v41, "]", "", -1)
v43 := regexp.MustCompile(",").Split(v42, -1)
for k4, s4 := range v43 {
speed[k4] = s4
fmt.Println(k4, ",", lat[k4], ",", lng[k4], ",", speed[k4])
}
}
}
ODデータ(csv):20220518weekday
領域データ(csv):yamaguchi_area
出力データ(csv):new_20220518weekday
その他: 年齢を乱数を使って適当に作成しているコードも入っている
// ~/yamaguchi/src_try1/others/main61.go
// Usage: go run main61.go 20220518weekday.csv new_20220518weekday.csv
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"os"
"strconv"
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("yamaguchi_area.csv")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer file.Close()
r := csv.NewReader(file)
rows, err := r.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
str := "SELECT ST_Covers(st_geomfromtext('POLYGON(("
// 行ごとに
for i, row := range rows {
if i == 0 {
continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
}
str += row[1] + " " + row[2] + ", " // rowのままで取り出せば、文字列になっている
}
str1 := str[:len(str)-2] + "))'),st_geomfromtext('LINESTRING(" // 上記の最後の", "を削除して、文字列を追加
dbMap, err := sql.Open("postgres",
"user=postgres password=password host=192.168.0.23 port=15432 dbname=yama_db sslmode=disable")
log.Println("------------------ map db open ------------------")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("OpenError: ", err)
}
defer dbMap.Close()
///////////////////////////////////////
//file2, err2 := os.Open("20220518weekday.csv")
file2, err2 := os.Open(os.Args[1]) // 第1パラメータ
if err2 != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
defer file2.Close()
r2 := csv.NewReader(file2)
rows2, err2 := r2.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
file3, err3 := os.Create(os.Args[2]) // 第2パラメータ
if err3 != nil {
panic(err)
}
w := csv.NewWriter(file3)
var id int
for _, row := range rows2 {
//if i == 0 {
// continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
//}
str2 := str1 + row[0] + " " + row[1] + ", " + row[2] + " " + row[3]
str2 += ")'))"
fmt.Println(str2)
rows1, err := dbMap.Query(str2)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer rows1.Close()
//var dt string
var dt bool
for rows1.Next() {
if err := rows1.Scan(&dt); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// fmt.Println(dt)
if dt {
//if err := rows.Scan(&id, &age, &type1, &departure_name, &departure_number, &departure_lat, &departure_lng, &arrival_name, &arrival_number, &arrival_lat, &arrival_lng); err != nil {
// fmt.Println(err)
// 上記のSQLのフォームと同じ形でcsvファイルを作る
var age int
fmt.Println("row[4]:", row[4])
// id_str := strconv.Itoa(id) // idを文字列に
if row[4] == "10-15" {
age = 10 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "15-29" {
age = 15 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "20-24" {
age = 20 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "25-29" {
age = 25 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "30-34" {
age = 30 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "35-39" {
age = 35 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "40-44" {
age = 40 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "44-49" {
age = 45 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "50-54" {
age = 50 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "55-59" {
age = 55 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "60-64" {
age = 60 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "65-69" {
age = 65 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "70-74" {
age = 70 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "75-80" {
age = 75 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "80-84" {
age = 80 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "85-89" {
age = 85 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "90-94" {
age = 90 + rand.Intn(5)
} else if row[4] == "95-99" {
age = 95 + rand.Intn(5)
} else {
age = 15 + rand.Intn(65) // 15箸キ79までの乱数
}
type1 := "resident"
departure_name := ""
_row1, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(row[1], 64)
_row0, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(row[0], 64)
departure_number, departure_lng, departure_lat := fixPosition(dbMap, _row1, _row0) // row[1], row[0]の順番に注意
arrival_name := ""
_row3, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(row[3], 64)
_row2, _ := strconv.ParseFloat(row[2], 64)
arrival_number, arrival_lng, arrival_lat := fixPosition(dbMap, _row3, _row2) // row[3], row[2]の順番に注意
output := []string{fmt.Sprint(id), fmt.Sprint(age), type1, departure_name, fmt.Sprint(departure_number), fmt.Sprint(departure_lat), fmt.Sprint(departure_lng), arrival_name, fmt.Sprint(arrival_number), fmt.Sprint(arrival_lat), fmt.Sprint(arrival_lng)}
//output := []string{row[0], row[1], row[2], row[3], row[4]}
fmt.Println("output:", output)
if err = w.Write(output); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
id++ // idの加算
}
}
err = rows1.Err()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer w.Flush()
if err := w.Error(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
}
// 指定した座標に近いDB上の座標を取得
func fixPosition(db *sql.DB, _x1, _y1 float64) (int, float64, float64) {
// Scan用の仮変数
var source int
var longitude float64
var latitude float64
var dist float64
upperLimitMeter := 1500.0 // 近傍ノードの上限を1500 mに設定
str := fmt.Sprintf(
// 修正前: ways (道) の中から最近傍を取得
// "SELECT source, x1 AS longitude, y1 AS latitude, ST_Distance('SRID=4326;POINT(%v %v)'::GEOGRAPHY, the_geom) AS dist FROM ways WHERE ST_DWithin(the_geom, ST_GeographyFromText('SRID=4326;POINT(%v %v)'), %.1f) ORDER BY dist LIMIT 1",
// 修正後: ways_vertices_pgr (点座標) の中から最近傍を取得
"SELECT id AS source, lon AS longitude, lat AS latitude, ST_Distance('SRID=4326;POINT(%v %v)'::GEOGRAPHY, the_geom) AS dist FROM ways_vertices_pgr WHERE ST_DWithin(the_geom, ST_GeographyFromText('SRID=4326;POINT(%v %v)'), %.1f) ORDER BY dist LIMIT 1",
_x1, _y1, _x1, _y1, upperLimitMeter,
)
//fmt.Println(str)
rows, err := db.Query(str)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer rows.Close()
foundGoodMapNode := false
for rows.Next() {
foundGoodMapNode = true
if err := rows.Scan(&source, &longitude, &latitude, &dist); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
//fmt.Println(source, longitude, latitude, dist)
}
if !foundGoodMapNode {
log.Println("Warning: in func fixPosition: Good Map Node not found for query point (",
_x1, ",", _y1, ")")
}
return source, longitude, latitude
}
strconv.FormatFloatだの、strconv.FormatIntだの、色々あるけど、
fmt.Sprint(x) xは、整数でも実数でも可
Keyword: golang csv write 書き出し ライン
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("yamaguchi_area.csv")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer file.Close()
r := csv.NewReader(file)
rows, err := r.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
str := "SELECT ST_Covers(st_geomfromtext('POLYGON(("
// 行ごとに
for i, row := range rows {
if i == 0 {
continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
}
str += row[1] + " " + row[2] + ", " // rowのままで取り出せば、文字列になっている
}
str1 := str[:len(str)-2] + "))'),st_geomfromtext('LINESTRING(" // 上記の最後の", "を削除して、文字列を追加
dbMap, err := sql.Open("postgres",
"user=postgres password=password host=192.168.0.23 port=15432 dbname=yama_db sslmode=disable")
log.Println("------------------ map db open ------------------")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("OpenError: ", err)
}
defer dbMap.Close()
///////////////////////////////////////
file2, err2 := os.Open("20220518weekday.csv")
if err2 != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
defer file2.Close()
r2 := csv.NewReader(file2)
rows2, err2 := r2.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
file3, err3 := os.Create("testtest.csv")
if err3 != nil {
panic(err)
}
w := csv.NewWriter(file3)
for _, row := range rows2 {
//if i == 0 {
// continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
//}
str2 := str1 + row[0] + " " + row[1] + ", " + row[2] + " " + row[3]
str2 += ")'))"
//fmt.Println(str2)
rows1, err := dbMap.Query(str2)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer rows1.Close()
//var dt string
var dt bool
for rows1.Next() {
if err := rows1.Scan(&dt); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// fmt.Println(dt)
if dt {
output := []string{row[0], row[1], row[2], row[3], row[4]}
//fmt.Println("output:", output)
if err = w.Write(output); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
}
err = rows1.Err()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer w.Flush()
if err := w.Error(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
}重要なのは、以下のコード
file3, err3 := os.Create("testtest.csv")
if err3 != nil {
panic(err)
}w := csv.NewWriter(file3)
output := []string{row[0], row[1], row[2], row[3], row[4]}
//fmt.Println("output:", output)if err = w.Write(output); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}defer w.Flush()
簡単にできるみたいです。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
//fmt.Printf("args count: %d\n", len(os.Args))
//fmt.Printf("args : %#v\n", os.Args)
// これでも拾えるし
for i, v := range os.Args {
fmt.Printf("args[%d] -> %s\n", i, v)
}
// こんな風にダイレクトにも取れる
fmt.Println(os.Args[1])
fmt.Println(os.Args[2])
}出力結果
PS C:\Users\ebata\yamaguchi\src_try1\others> go run main7.go test1 test2
args[0] -> C:\Users\ebata\AppData\Local\Temp\go-build2152603201\b001\exe\main7.exe
args[1] -> test1
args[2] -> test2
test1
test2
keyword: postgres postgis st_geomfromtext ST_Covers POLYGON LINESTRING
早い話、
postgres=# \c yama_db
psql (13.4, server 12.5 (Debian 12.5-1.pgdg100+1))
You are now connected to database "yama_db" as user "postgres".yama_db=# SELECT ST_Covers(st_geomfromtext('POLYGON((34.15131035 131.5194525, 34.16270729 131.5152409, 34.16516798 131.5115994, 34.16898442 131.5047413, 34.17907707 131.5010998, 34.18354557 131.4989149, 34.18561453 131.5025188, 34.18856404 131.5058416, 34.18909138 131.5050188, 34.19687848 131.5103978, 34.19927298 131.5072766, 34.20121465 131.510747, 34.20300086 131.5120785, 34.20536452 131.5096798, 34.20975399 131.5068729, 34.20709501 131.5009018, 34.20388724 131.5048315, 34.20194564 131.5047294, 34.19785124 131.4988093, 34.20194564 131.4969721, 34.20528011 131.4932975, 34.20114366 131.4948286, 34.19802009 131.4962576, 34.19894873 131.4931955, 34.19705211 131.4916877, 34.19973769 131.4886834, 34.19579714 131.490747, 34.19717761 131.4888048, 34.19802009 131.4962576, 34.20061613 131.483555, 34.19383935 131.482506, 34.19306821 131.4800321, 34.18962489 131.4802896, 34.20041552 131.4735871, 34.19870882 131.4691668, 34.19193378 131.4719122, 34.19281714 131.4631425, 34.18750372 131.4649829, 34.18208468 131.4692086, 34.17814677 131.4619382, 34.18089338 131.4606752, 34.18352048 131.465583, 34.18537135 131.4575717, 34.18358019 131.4532773, 34.17689286 131.4597008, 34.17568909 131.4574644, 34.17805351 131.453254, 34.18115671 131.4490436, 34.18094562 131.4462621, 34.17766341 131.4457491, 34.17637565 131.444856, 34.17452943 131.4472807, 34.17400259 131.4457099, 34.1745741 131.4435783, 34.17591761 131.4391215, 34.17349927 131.4370465, 34.171469 131.4367036, 34.17997306 131.4313284, 34.17831615 131.4270193, 34.16993073 131.4276566, 34.17045141 131.4197235, 34.16662955 131.4242344, 34.17054098 131.4093664, 34.16585321 131.4150321, 34.16292695 131.4256418, 34.16209086 131.4305497, 34.15853738 131.4324262, 34.1555247 131.431539, 34.1368104 131.4231705, 34.13155312 131.4262604, 34.13252285 131.4303061, 34.12981919 131.4361751, 34.12994592 131.4412276, 34.13256509 131.4488319, 34.13167796 131.4539864, 34.13486474 131.4591635, 34.13933143 131.4660729, 34.14099198 131.4710403, 34.14447279 131.4734114, 34.14677254 131.4766944, 34.14983145 131.488296, 34.14860698 131.5025144, 34.15034783 131.5173554, 34.15131035 131.5194525))'),st_geomfromtext('LINESTRING(34.17282136235268 131.4810495539796, 34.17234106467595 131.47746432882846)'));
というSQL文をGoプログラムで作る。
(1)csvファイル(84点)からなる領域を作っておいて、エリアデータ
(2)ODデータを直線として取り込み、直線データ
(3)上記(2)の直線が、上記(1)の領域に入っているかどうかを調べて、入っている場合は標準出力で出力する
// ~/yamaguchi/src_try1/others/main6.go
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"encoding/csv"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("yamaguchi_area.csv")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer file.Close()
r := csv.NewReader(file)
rows, err := r.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
str := "SELECT ST_Covers(st_geomfromtext('POLYGON(("
// 行ごとに
for i, row := range rows {
if i == 0 {
continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
}
str += row[1] + " " + row[2] + ", " // rowのままで取り出せば、文字列になっている
}
str1 := str[:len(str)-2] + "))'),st_geomfromtext('LINESTRING(" // 上記の最後の", "を削除して、文字列を追加
dbMap, err := sql.Open("postgres",
"user=postgres password=password host=192.168.0.23 port=15432 dbname=yama_db sslmode=disable")
// log.Println("------------------ map db open ------------------")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("OpenError: ", err)
}
defer dbMap.Close()
///////////////////////////////////////
file2, err2 := os.Open("20220518weekday.csv")
if err2 != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
defer file2.Close()
r2 := csv.NewReader(file2)
rows2, err2 := r2.ReadAll() // csvを一度に全て読み込む
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err2)
}
for _, row := range rows2 {
//if i == 0 {
// continue // CSVのヘッダー行を無視
//}
str2 := str1 + row[0] + " " + row[1] + ", " + row[2] + " " + row[3]
str2 += ")'))"
//fmt.Println(str2)
rows1, err := dbMap.Query(str2)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer rows1.Close()
//var dt string
var dt bool
for rows1.Next() {
if err := rows1.Scan(&dt); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// fmt.Println(dt)
if dt {
output := row[0] + "," + row[1] + "," + row[2] + "," + row[3] + "," + row[4]
fmt.Println(output)
}
}
}
}